Introduction :
Docker is one of the most popular container-based platforms attracting the attention of many development teams. More and more companies are switching to Docker due to its reliability, performance, and functionality. Therefore, it is essential to understand this open-source containerization software and the underlying components powering it. In this article, you will learn what Docker is, what are Docker's most important components, and the pros and cons of using the platform.
What Are Containers?
Docker containers are lightweight virtualized runtime environments for running applications. Each container represents a package of software that contains code, system tools, runtime, libraries, dependencies, and configuration files required for running a specific application. They are independent and isolated from the host and other instances running on the host. Containers are based on Docker images. You build a container by running an image on the Docker Engine. As these are the most common Docker terms, make sure you understand the difference between Docker images and Docker containers. The same hardware can host multiple containers. Unlike virtual machines, containers virtualize at the application level. Therefore, they share the OS kernel with the host and virtualize an operating system on top of it. This means you use fewer resources and maintain lightweight virtual environments that are quick and easy to configure.
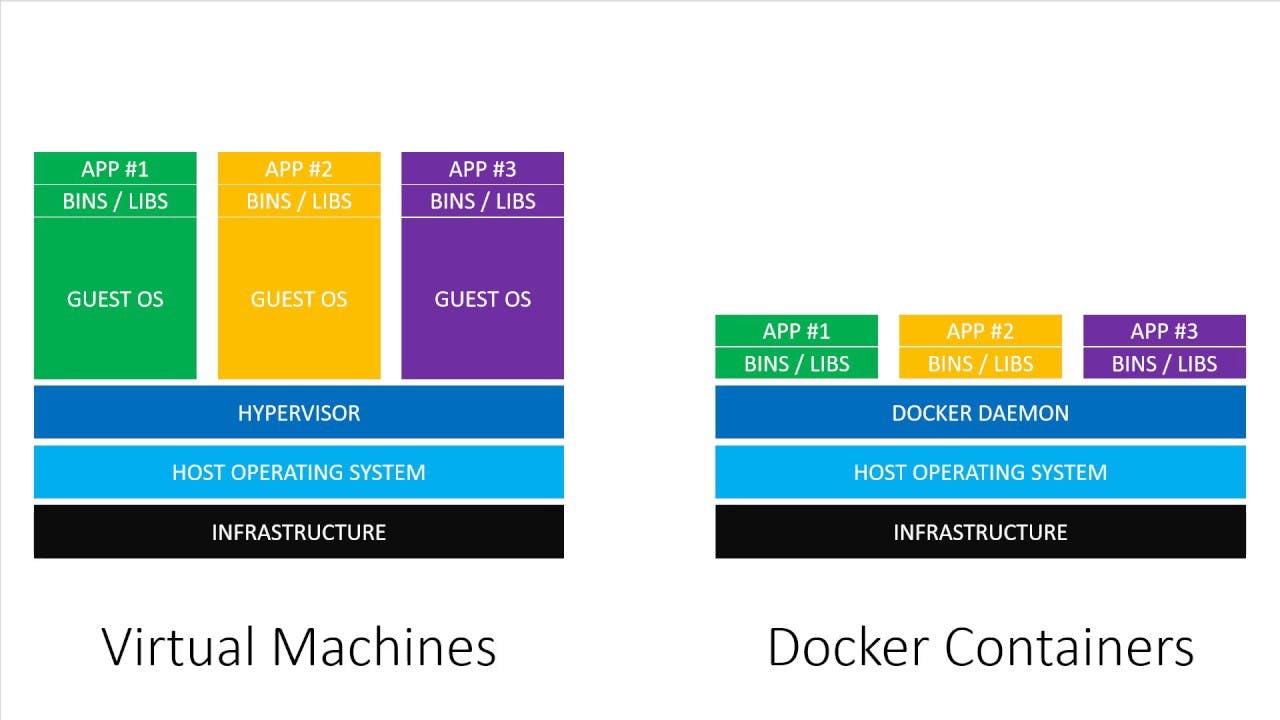
Apart from being system agnostic, containers are quick and easy to start up, configure, add, stop, and remove. Developers can work on the same application in different environments knowing this will not affect its performance. Additionally, they can share data between containers using data volumes.
What Is Docker Used For?
Docker is used for:
Develop applications that work on any OS
Easy to share applications among teams
Easy to scale across multiple servers
Large applications can be broken into multiple containers - one for each microservice
A great solution for Cloud Computing
Big community and library of Docker Images
A cost-effective alternative to virtual machines.
A version control system for an application.
Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop, formerly known as Docker for Windows and Docker for Mac, is an application that allows you to start creating and running containers on Windows and Mac within minutes. It is a simple way of installing and setting up the entire Docker development environment. It includes Docker Engine, Docker Compose, Docker CLI client, Docker Content Trust, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper.
The tool is used for building and sharing containerized applications and microservices in multiple languages and frameworks, on any cloud platform.
To learn more, check out Docker's official documentation on Docker Desktop.
Docker Advantages
Consistency. Docker ensures reliability that your app runs the same across multiple environments. Developers working on different machines and operating systems can work together on the same application without environmental issues.
Automation. The platform allows you to automate tedious, repetitive tasks and schedule jobs without manual intervention.
Faster deployments. Since containers virtualize the OS, there is no boot time when starting up container instances. Therefore, you can do deployments in a matter of seconds. Additionally, you can share existing containers to create new applications.
Support of CI/CD. Docker works well with CI/CD practices as it speeds up deployments, simplifies updates, and allows teammates to work efficiently together.
Rollbacks and image version control. A container is based on a Docker image which can have multiple layers, each representing changes and updates on the base. Not only does this feature speed up the build process, but it also provides version control over the container. This allows developers to roll back to a previous version if the need arises.
Modularity. Containers are independent and isolated virtual environments. In a multi-container application, each container has a specific function. By segregating the app, developers can easily work on a particular part without taking down the entire app.
Resource and cost-efficiency. As containers do not include guest operating systems, they are much lighter and smaller than VMs. They take up less memory and reuse components thanks to data volumes and images. Also, containers don't require large physical servers as they can run entirely on the cloud.
Docker Disadvantages
No graphical interface. Docker is not the best choice if you want to run apps that require a graphical interface. It is mainly for hosting applications that run on the command line.
Security issues. Although Docker provides security by isolating contains from the host and each other, there are certain Docker-specific security risks. Many potential security issues may arise while working with containers, so make sure to adopt the best Docker security practices that can help you prevent attacks and privilege breaches.
Learning curve. Even developers experienced with the VM infrastructure need some time to get used to Docker concepts and how they work. If switching to Docker, make sure to take into account the necessary learning curve.
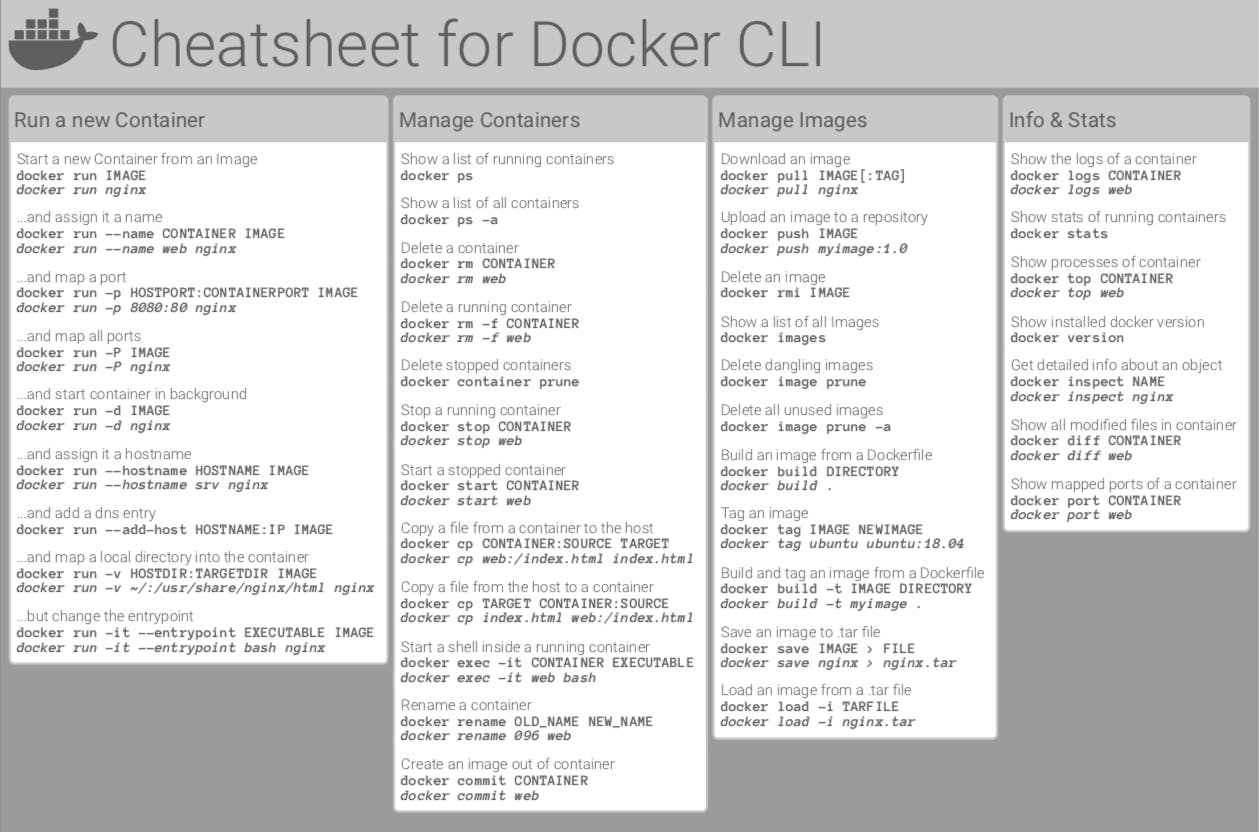
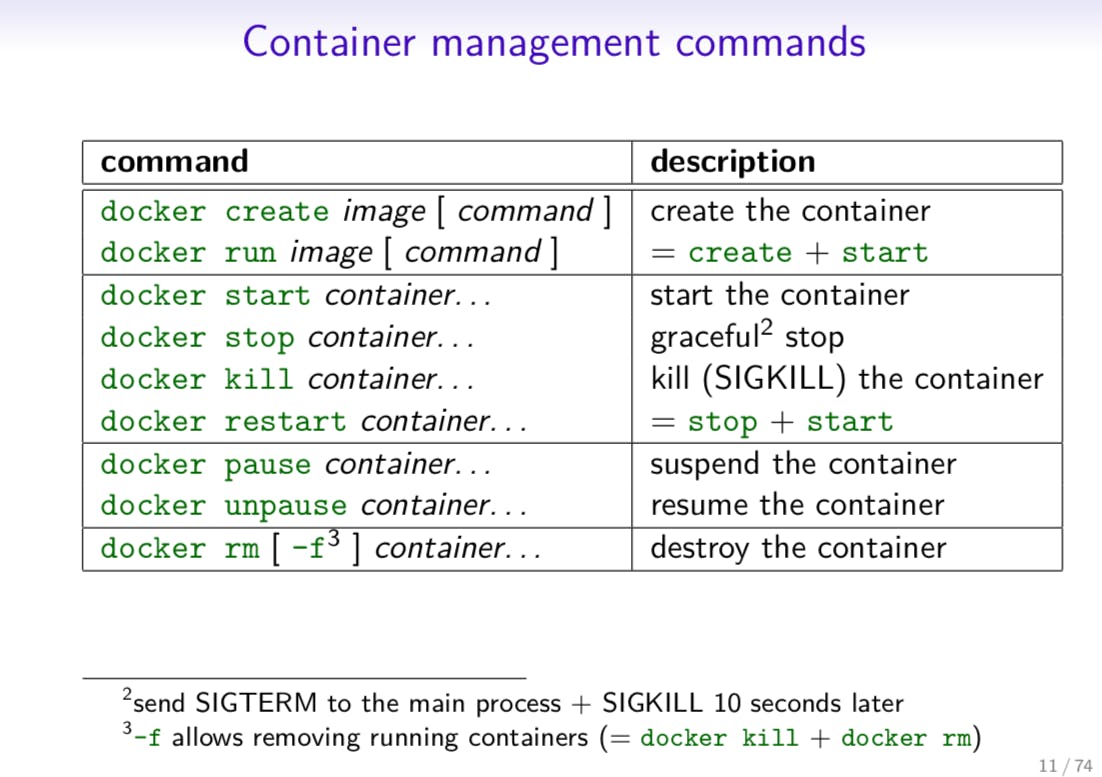
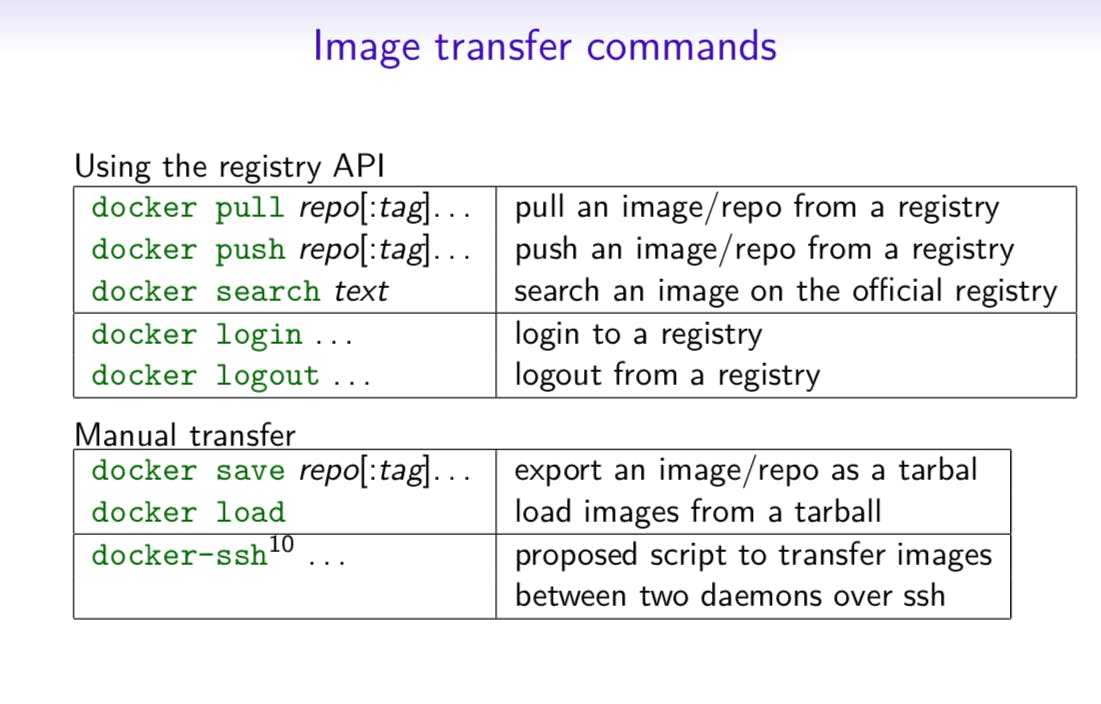
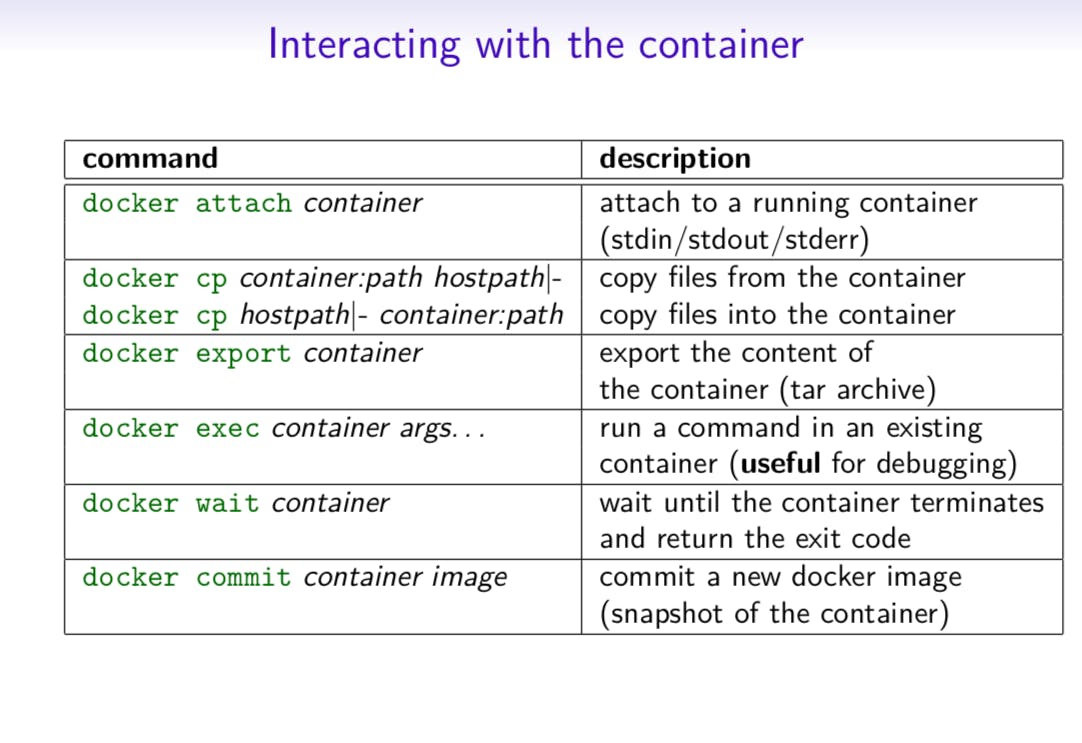
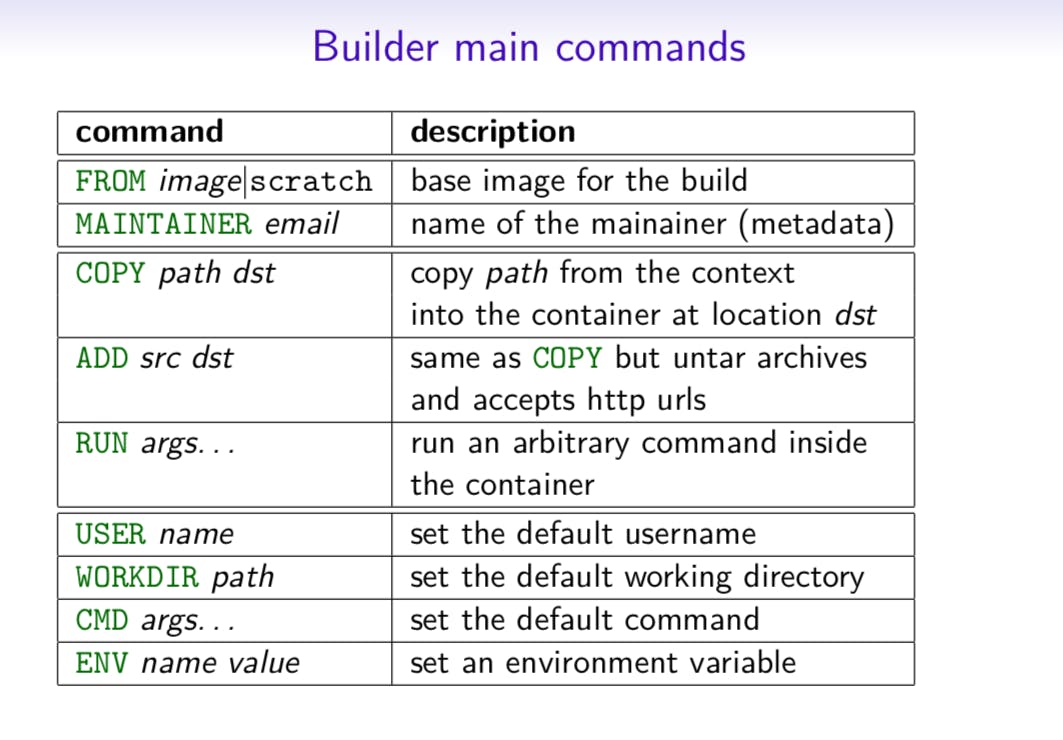
The Ultimate Docker Cheat Sheet
Conclusion
In this article, you learned all about Docker, why it is useful in software development, and how you can start using it. Make the most of Docker's advantages and utilize this powerful containerization platform.
Thanks For Reading! :)
- Rushikesh Mashidkar💕

